Brain Story – Overload
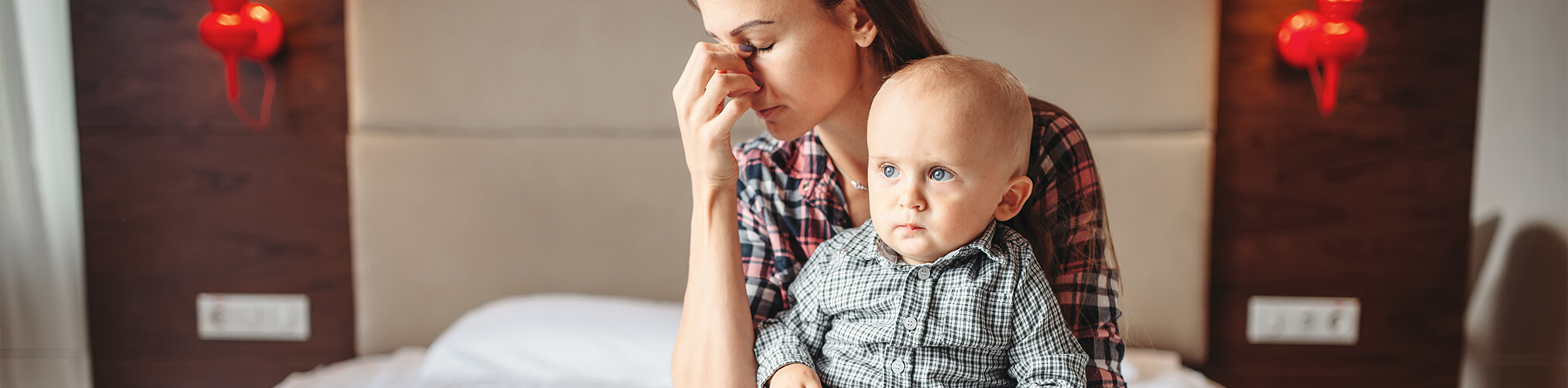
For this part of ‘Sharing the Science’, imagine trucks delivering lots of cargo to parents and caregivers, resulting in an overload of burden and stress.

When a truck carries too much weight, it can be overloaded to the point of breaking down.
When parents are burdened with stresses like poverty or lack of support, the weight of these problems can overload their mental and emotional capacity to take care of their children’s needs.

Reducing stresses for parents and caregivers is crucial
Some overloaded parents may be reluctant to ask for help for fear of their child being removed from their care. So, it’s important for professionals to recognize the load that parents and caregivers might be carrying, direct them to appropriate support services and consider how to reduce unnecessary weight and strain by:
- Taking time to understand a parent or caregiver’s position and providing support.
- Encouraging parents and caregivers to seek out support from the community and family members or guide them to support directly. These community resources can be effective in buffering children’s toxic stress response (Franke, 2014).
- Providing direct support to parents and caregivers as soon as problems are identified.
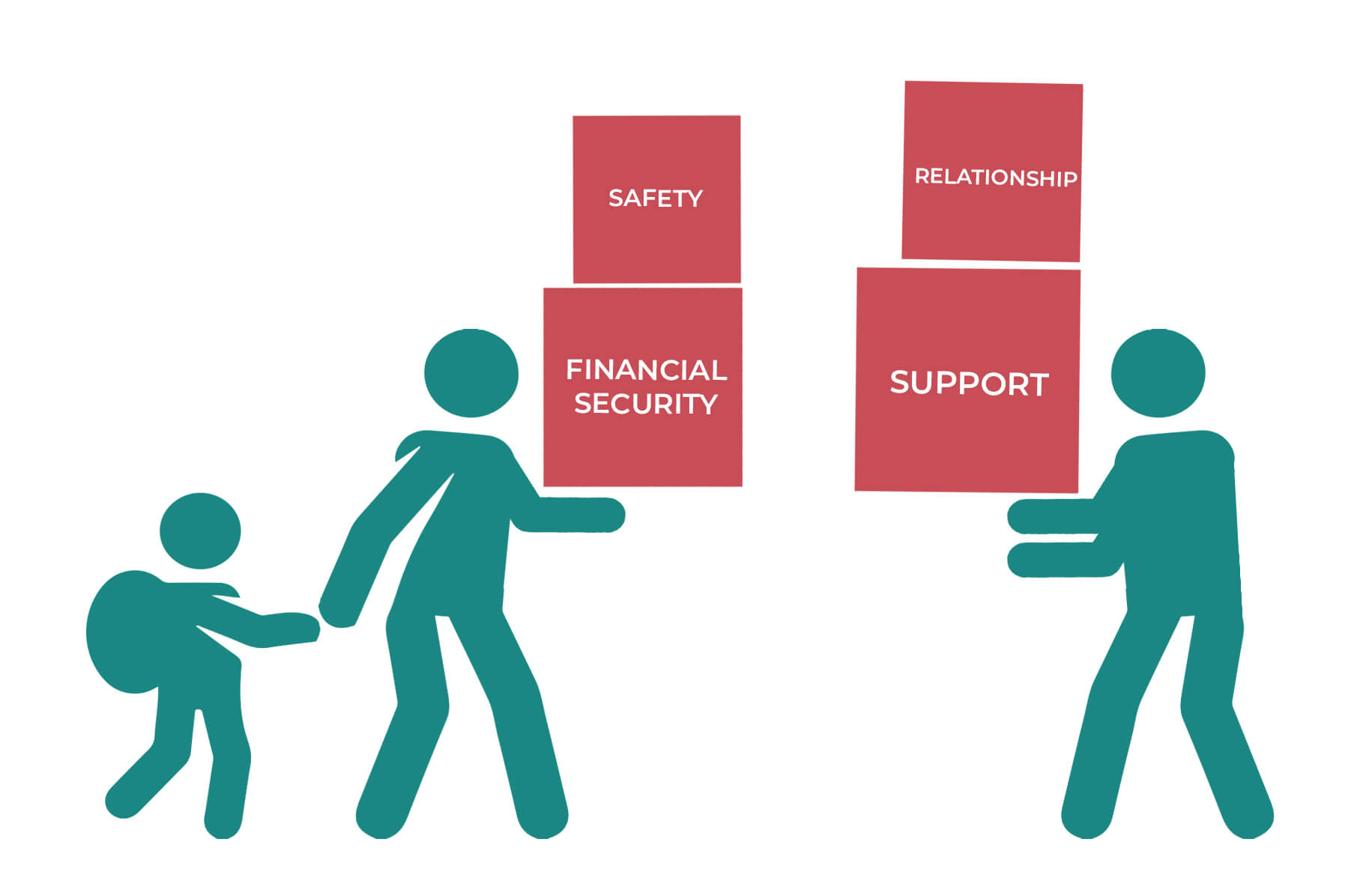
Just as we can lighten an overloaded truck’s load by bringing in other trucks or moving some things by train, we can lighten parents’ and caregivers’ mental stresses through a range of support services.

Get Brain Story certified!
The Brain Story Certification course is for anyone seeking a deeper understanding of brain development and its consequences for lifelong health. This self-paced online course is free and open to the public. The course is also designed for professionals seeking certification in a wide range of fields and includes 30 hours of instruction time.
References & Sources
- Center on the Developing Child (2013) Innovating in Early Head Start: Can Reducing Toxic Stress Improve Outcomes for Young Children? [Accessed 8/11/2019].
- Crowley, Kevin (2017) Child Development: a practical introduction. London: SAGE Publications Ltd.
- Diamond, A (2013) Executive Functions Annual Review of Psychology, 64: 135-168.
- Franke H.A (2014) Toxic Stress: Effects, Prevention and Treatment. Children, 1(3): 390–402.
- Kendall-Taylor, N and Stanley, K (2018) Seeing Context through Metaphor: Using Communications Research to Bring a Social Determinants Perspective to Public Thinking about Child Abuse and Neglect. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(1): 8-14.
- National Commission on Domestic and Sexual Violence and Multiple Disadvantage (2019) Breaking Down the Barriers (PDF). [s.l.]: National Commission on Domestic and Sexual Violence and Multiple Disadvantage.
- Siegel, D. J. and Bryson, T. P. (2012) The Whole-Brain Child 12 Revolutionary Strategies to Nurture Your Child’s Developing Mind, Survive Everyday Parenting Struggles, and Help Your Family Thrive. London: Robinson.
- Shonkoff, J.P. et al (2004) Young Children Develop in an Environment of Relationships. Cambridge: Center on the Developing Child, Harvard University.
- Shonkoff, J.P. et al (2008) The Timing and Quality of Early Experiences Combine to Shape Brain Architecture Working Paper 5. Cambridge: Center on the Developing Child, Harvard University.
- Shonkoff, J.P., Boyce, W.T. and McEwen, B.S. (2009) Neuroscience, molecular biology, and the childhood roots of health disparities: building a new framework for health promotion and disease prevention, Journal of the American Medical Association, 301 (21), 2252-2259.
- Shonkoff, J.P. et al (2011) Building the Brain’s “Air Traffic Control” System: How Early Experiences Shape the Development of Executive Function Working Paper 11. Cambridge: Center on the Developing Child, Harvard University.
- Shonkoff, J.P. et al (2014), Excessive Stress Disrupts the Architecture of the Developing Brain Working Paper 3. Cambridge: Center on the Developing Child, Harvard University.
- Shonkoff, J.P. et al (2015) Supportive Relationships and Active Skill-Building Strengthen the Foundations of Resilience Working Paper 13. Cambridge: Center on the Developing Child, Harvard University.
- Shonkoff, J.P. et al (2018) Understanding Motivation: Building the Brain Architecture That Supports Learning, Health, and Community Participation Working Paper 14. Cambridge: Center on the Developing Child, Harvard University.
